本文介绍了质数的判别以及筛法相关的算法知识。
质数 的定义:在大于 1 的整数中,如果只能被 1 和本身整除,就被称为质数,或素数。
1. 质数的判定——试除法 方法 1:基本方法 是最笨的方法,复杂度为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 bool is_prime (int n) if ( n < 2 ) return false ; for (int i = 2 ; i < n ; i++){ if ( n % i == 0 ) return false ; } return true ; }
方法 2:优化方法 性质:如果
所以我们可以只枚举一对中较小的那一个。那么只需要枚举验证,
AcWing 866: 试除法判定质数 问题链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/868/
题目 :
给定 n 个正整数
数据范围:
解题思路 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int n, x;bool is_prime (int n) if (n < 2 ) return false ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n / i; i++) { if (n % i == 0 ) return false ; } return true ; } void solve () cin >> n; while (n--) { cin >> x; if (is_prime (x)) cout << "Yes" << endl; else cout << "No" << endl; } } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
注意:判断条件处最佳写法为: i <= n / i 。
不推荐写成 i <= sqrt(n) 因为每次都会计算一次 sqrt,非常的慢,影响执行速度;
不推荐写成 i * i <= n 因为当
2. 分解质因数——试除法 质因数:是指能够整除给定正整数的质数。
1 没有质因子。 5 只有 1 个质因子,5 本身。(5 是质数) 6 的质因子是 2 和 3。(6 = 2 × 3) 2、4、8、16 等只有 1 个质因子:2。(2 是质数,4 =2²,8 = 2³,如此类推) 10 有 2 个质因子:2 和 5。(10 = 2 × 5) 从小到大尝试 n 的所有的因数。 只需要枚举到 sqrt(n) 即可(因为 n 中最多只包含一个大于 n 的质因数)
时间复杂度最慢是
AcWing 867: 分解质因数 问题链接 :https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/869/
题目 :
给定
数据范围:
解题思路 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;void divide (int x) for (int i = 2 ; i <= x / i; i ++ ) if (x % i == 0 ) { int s = 0 ; while (x % i == 0 ) x /= i, s ++ ; cout << i << ' ' << s << endl; } if (x > 1 ) cout << x << ' ' << 1 << endl; cout << endl; } int main () int count; cin >> count; while (count--){ int n; cin >> n; divide (n); } return 0 ; }
3. 质数筛选 备注:质数其实没有那么多。100 万以内,大概有 8 万个质数。
方法 1:基本筛法 这种筛选方法的时间复杂度为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 1000010 ;int primes[N] , cnt ;bool st[N];void get_primes (int n) for (int i = 2 ; i <= n ; i++ ){ if (!st[i]){ primes[ cnt ++ ] = i ; } for (int j = i + i ; j <= n ; j += i) st[j] = true ; } } int main () int n; cin >> n ; get_primes (n); cout << cnt << endl; return 0 ; }
方法 2:埃氏筛法 质数定理 :1 ~ n 中,有
这个方法中的时间复杂度约为
这个算法也称为 埃氏筛法 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 1000010 ;int primes[N] , cnt ;bool st[N];void get_primes (int n) for (int i = 2 ; i <= n ; i++ ){ if (!st[i]){ primes[cnt++] = i; for (int j = i+i ; j <= n ; j += i) st[j] = true ; } } } int main () int n; cin >> n; get_primes (n); cout << cnt << endl; return 0 ; }
方法 3:线性筛法 n 只会被最小质因子筛掉
每一个数只会被最小质因子筛一次,所以是线性的时间复杂度为
注:下面两个代码的 primes 数组声明方式不一样。一个用普通数组,一个用 vector。供参考
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 1000010 ;int primes[N] , cnt ;bool st[N];void get_primes (int n) for (int i = 2 ; i <= n ; i++ ){ if (!st[i]) primes[cnt ++] = i; for (int j = 0 ; primes[j] <= n / i ; j ++){ st[ primes[j] * i] = true ; if ( i % primes[j] == 0 ) break ; } } } int main () int n; cin >> n; get_primes (n); cout << cnt << endl; return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 1000010 ;int cnt;bool st[N];vector<int > primes; void get_primes (int n) for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { if (!st[i]) primes.push_back (i); for (int j = 0 ; primes[j] <= n / i; j++) { st[primes[j] * i] = true ; if (i % primes[j] == 0 ) break ; } } } int main () int n; cin >> n; get_primes (n); cout << primes.size () << endl; }
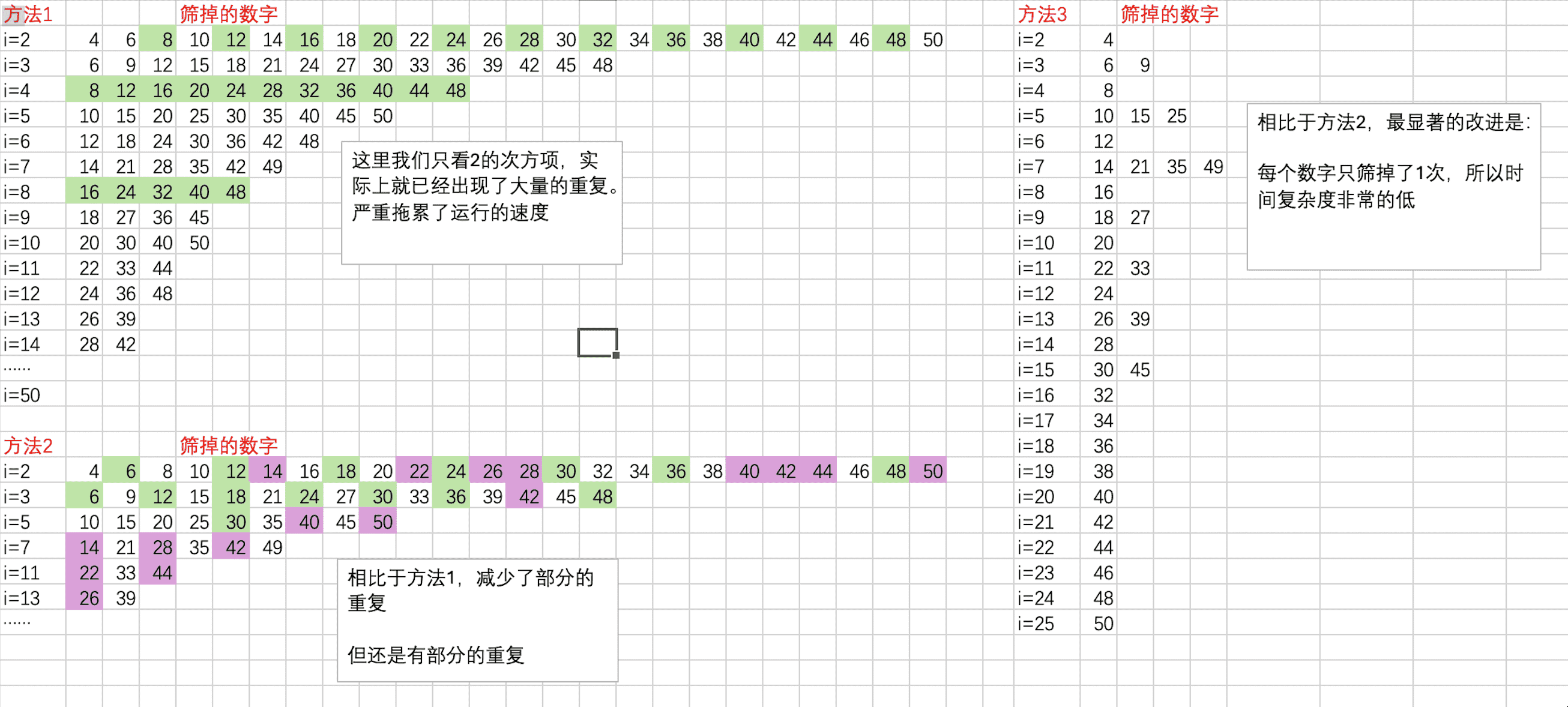
备注:为什么线性筛法的时间复杂度这么低? 举一个例子:我们来筛选出 50 以内的质数。三个方法筛掉的数字为下图所示:
上图分别显示了方法 1~方法 3 在实际运算中的重复程度。可以发现,多余的时间复杂度其实全是因为重复遍历所导致的。而线性筛法真正做到了每个数只看一次,所以是