本文是 AtCoder Beginner Conteset(ABC)384 的总结笔记。
A - aaaadaa Problem:A - aaaadaa
签到题。将字符串a 的字符全部改成 b。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int n;char a, b;string s; void solve () cin >> n >> a >> b >> s; for (auto & x : s) if (x != a) x = b; cout << s << endl; } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
B - ARC Division Problem:B - ARC Division
模拟题。
按照题目要求做条件判断即可。
如果参加的是 div1 并且当前 rating 在 如果参加的是 div2 并且当前 rating 在 其他情况直接跳过 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int n, r;int d, a;bool check_div1 (int r) if (r >= 1600 && r <= 2799 ) return true ; return false ; } bool check_div2 (int r) if (r >= 1200 && r <= 2399 ) return true ; return false ; } void solve () cin >> n >> r; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> d >> a; if (d == 1 && check_div1 (r)) r += a; else if (d == 2 && check_div2 (r)) r += a; else continue ; } cout << r << endl; } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
C - Perfect Standings Problem:C - Perfect Standings
位运算 + STL
题目: A B C D E 题分别对应 a b c d e 五个分值。
从只做出 A 题到全部做完 ABCDE ,共有 31 种组合情况。
按照分值从大到小输出各种做题的可能性,分值相同的时候,按照字典序输出。
思路: 这道题虽然使用最暴力的手工枚举也可以做,但是太过麻烦。下面是更加通用的方法。
需要解决两个问题:
如何枚举所有的做题状态?
本题总共有五位,所以可以使用一个五位的二进制数就可以枚举出各个题的解答状态。
如何按照分数降序 和 字典序升序的方式排列。
使用 struct 的时候,单独定义 cmp 比较算子。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int a[5 ];struct Score { int s; int st; string str; } s[50 ]; bool cmp (const Score& a, const Score& b) if (a.s != b.s) { return a.s > b.s; } return a.str < b.str; } string make_str (int x) { string s = "" ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) if (x >> i & 1 ) s += 'A' + i; sort (s.begin (), s.end ()); return s; } int cal_score (int x) int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) if (x >> i & 1 ) res += a[i]; return res; } void solve () for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) cin >> a[i]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= 31 ; i++) { s[i].st = i; s[i].s = cal_score (i); s[i].str = make_str (i); } sort (s, s + 32 , cmp); for (int i = 0 ; i < 31 ; i++) cout << s[i].str << endl; } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
D - Repeated Sequence Problem:D - Repeated Sequence
思维题
题目: 给定长度为
是否能截取连续出子序列,使和恰好为
约束条件
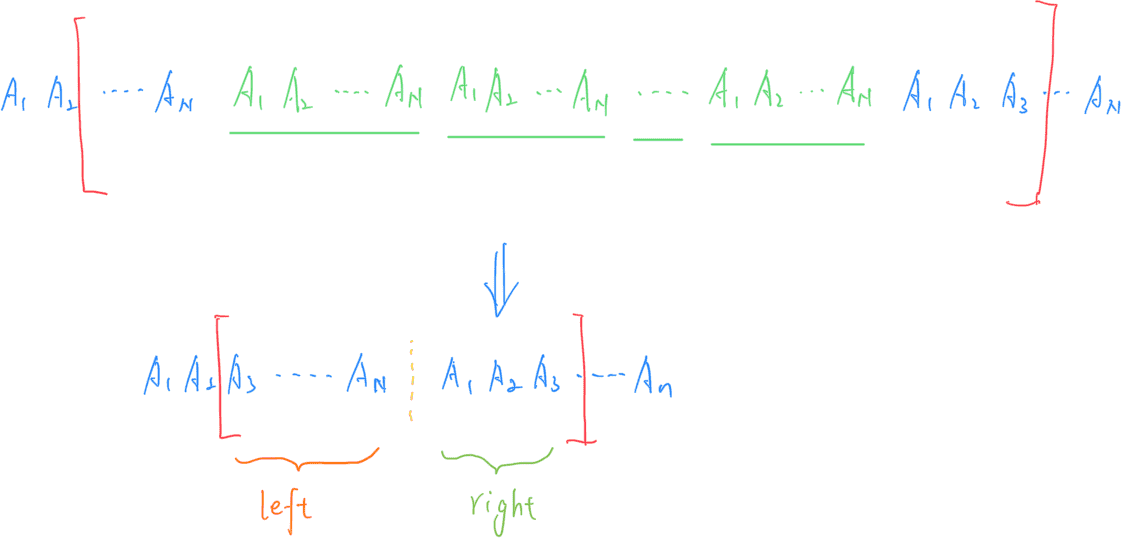
思路: 根据下图示例,我们可以发现,选取的子段由三部分组成:一个后缀,若干个周期 pattern,一个前缀。
由于任意的
如果去除中间重复的 pattern,最后一定会剩下左边的一部分 left 和右边的一部分 right。那么
问题转化为,能不能找到一个后缀和一个前缀,使二者的和等于
最后剩下的部分,和的范围应该是
所以我们依次遍历左边部分的后缀和,同时维护一个 set,判断 set 里面有没有我们想要的值即可。总时间复杂度为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 2e5 + 10 ;int A[N];LL sum[N]; LL n, s; set<LL> h; void solve () cin >> n >> s; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> A[i]; sum[i] = sum[i - 1 ] + A[i]; h.insert (sum[i]); } s %= sum[n]; sum[n + 1 ] = sum[n]; bool can = false ; for (int i = n + 1 ; i >= 1 ; i--) { LL left = sum[n + 1 ] - sum[i - 1 ]; LL right = s - left; if (h.count (right)) can = true ; if (h.count (right + sum[n])) can = true ; if (can) break ; } if (can) cout << "Yes" << endl; else cout << "No" << endl; } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
E - Takahashi is Slime 2 Problem:E - Takahashi is Slime 2
优先队列 BFS。本题和 ABC 383 的 E - Sinking Land 题目非常相似。
题目: 给定
从起点向四方向移动。只有数值res 的
求最大累加值。
约束条件:
思路: 标准的优先队列 BFS 题目。按照题目写即可。
需要注意的一个细节点:
题目要求“数值res 的s * X < res 的话,在本题规模下会溢出。这里只需要计算s < (res+X-1)/X 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int dx[4 ] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }, dy[4 ] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 };const int N = 510 ;LL g[N][N]; LL P, Q; LL H, W, X; LL res; bool st[N][N];struct Node { LL x, y, score; bool operator <(const Node& a) const { return score > a.score; } }; priority_queue<Node> que; void solve () cin >> H >> W >> X >> P >> Q; for (int i = 1 ; i <= H; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j <= W; j++) { cin >> g[i][j]; } que.push ((Node){P, Q, g[P][Q]}); st[P][Q] = true ; res = 0 ; while (que.size () && (res == 0 || que.top ().score < (res + X - 1 ) / X)) { Node now = que.top (); que.pop (); res += now.score; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int a = now.x + dx[i], b = now.y + dy[i]; if (a < 1 || a > H || b < 1 || b > W) continue ; if (st[a][b]) continue ; que.push ((Node){a, b, g[a][b]}); st[a][b] = true ; } } cout << res << endl; } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
F - Double Sum 2 Problem:F - Double Sum 2
数论题目。(这道题非常的抽象,很难理解)
题目: 给定正整数
给定序列
约束条件:
思路: 技巧:
整体思路:
定义 也就是说,
那么,如果 备注:这里可能稍微有点难理解。举个例子,一个数
最终所求的答案就是:将所有 细节问题处理:
根据上面的思路,于是问题就转变为:如何快速的求出
我们可以知道:
技巧:同余条件
所以当处理 j 位置时,我们希望知道:
在 在 为了方便计数求和,我们可以用一个以
map:
键 key: 值 value:在当前余数下出现的所有 因此,当我们要处理
若存在,就可以得到相匹配的
然后根据前面的公式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define int long long typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 2e5 + 10 , M = 2e7 + 10 ;int n;int a[N];int sum[M]; int cnt[M]; int d[30 ]; void solve () cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i]; int k = 1 ; for (int j = 0 ; j <= 24 ; j++) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int key = a[i] % k; sum[key] += a[i]; cnt[key]++; d[j] += sum[(k - a[i] % k) % k] + a[i] * cnt[(k - a[i] % k) % k]; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int key = a[i] % k; sum[key] = 0 ; cnt[key] = 0 ; } k = k * 2 ; } int res = 0 ; k = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= 24 ; i++) { res += (d[i] - d[i + 1 ]) / k; k *= 2 ; } cout << res << endl; } signed main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }