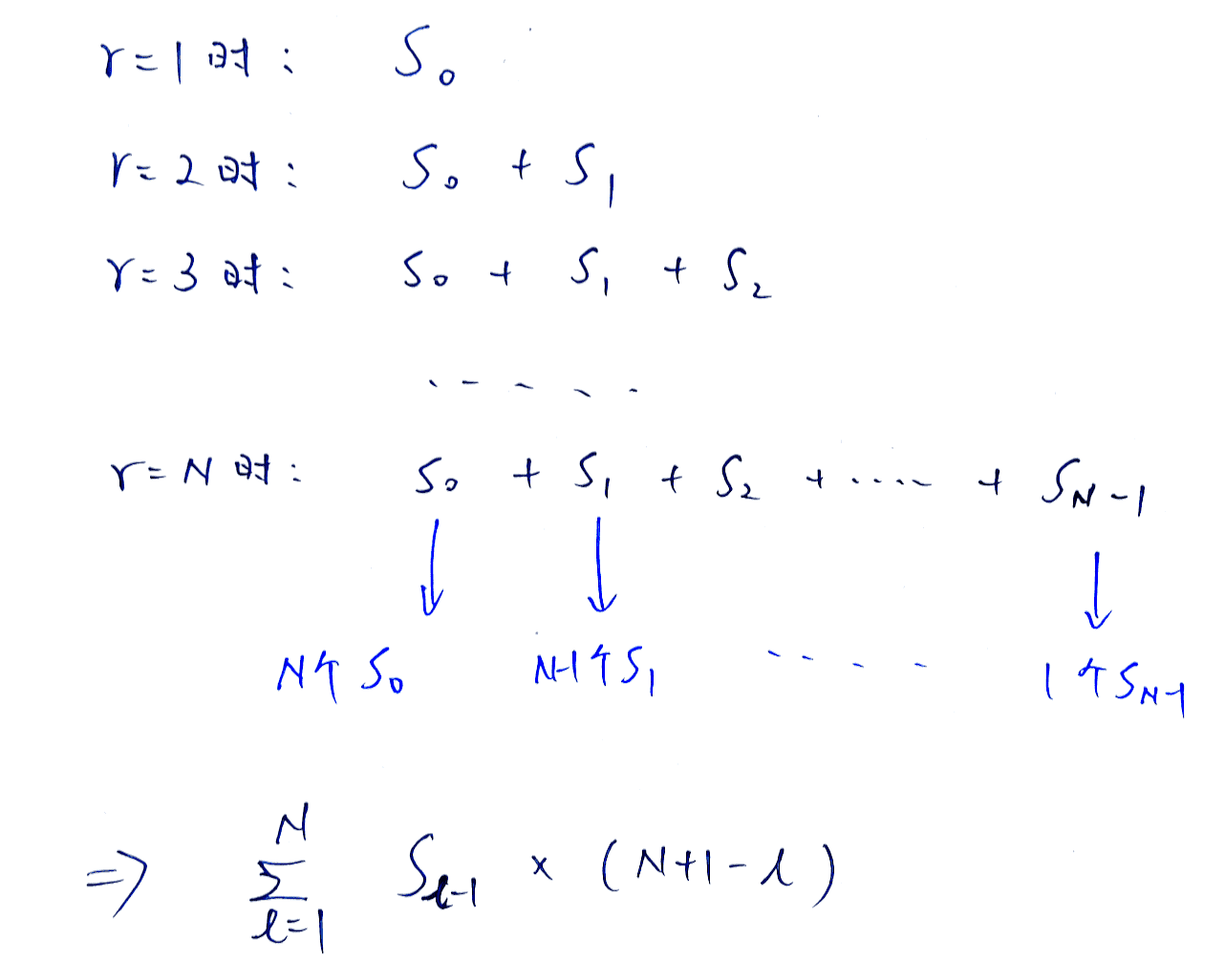本文是 AtCoder Beginner Conteset(ABC)378 的总结笔记。
A - Pairing Problem:A - Pairing
省略。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int f[4 ];void solve () for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int c; cin >> c; f[c]++; } int res = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= 4 ; i++) res += f[i] / 2 ; cout << res << endl; } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
B - Garbage Collection Problem:B - Garbage Collection
模拟题。
省略。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 110 ;int q[N], r[N];int n, Q;void solve () cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) cin >> q[i] >> r[i]; cin >> Q; for (int i = 1 , t, d; i <= Q; i++) { cin >> t >> d; int tmp = d % q[t]; if (tmp <= r[t]) cout << d + (r[t] - tmp) << endl; else cout << d + q[t] - tmp + r[t] << endl; } } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
C - Repeating Problem:C - Repeating
STL
输出一个数字前面,离他最近的相同数字的位置。没有就输出 -1。
思路非常的简单,使用一个 unordered_map 来存储每个数字的出现位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;int n, a;unordered_map<int , int > q; void solve () cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a; if (!q.count (a)) cout << -1 << " " ; else cout << q[a] << " " ; q[a] = i; } } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
D - Count Simple Paths Problem:D - Count Simple Paths
DFS。
一道非常标准的 DFS 题目。难度不大。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 15 ;string g[N]; bool st[N][N]; int n, m, k;int res;int dx[4 ] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }, dy[4 ] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 };void dfs (int x, int y, int k) if (k == 0 ) { res++; return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i]; if (a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > m) continue ; if (g[a][b] == '#' || st[a][b]) continue ; st[a][b] = true ; dfs (a, b, k - 1 ); st[a][b] = false ; } } void solve () cin >> n >> m >> k; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> g[i]; g[i] = " " + g[i]; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { if (g[i][j] == '#' ) continue ; st[i][j] = true ; dfs (i, j, k); st[i][j] = false ; } cout << res << endl; } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
E - Mod Sigma Problem Problem:E - Mod Sigma Problem
推公式 + 树状数组BIT
题目: 给定一组长度为
求
约束条件:
思路 : 本题整体需要解决下面两个问题:
问题 1:公式化简 我们定义带模前缀和 为
那么我们就可以将原公式转化为
根据常用的知识点:
,我们就可以将 mod 符号从公式中去除掉,原公式转化为:
备注:照理说前缀和中,
本题中使用的是带模前缀和,所以真实的
从上面公式可以发现,公式最后可以被拆成 3 个部分:
问题 2:使用 BIT 求逆序对 逆序对的定义是:找到所有的
如何使用 BIT 求逆序对的数量呢?
假设从左向右遍历数组,当处理到
这一步的时间复杂度为
总结: 本题的整体思路为:首先将公式进行推到化简,可以发现分别求出三个部分的值就可以得出最终的结果。最麻烦的是如何求整体的逆序对数量,这里使用了 BIT 的数据结构。
整体的时间复杂度为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 2e5 + 10 ;int n, m;int a[N]; int s[N]; int tr[N]; int lowbit (int x) return x & -x; } void add (int x, int k) x++; for (int i = x; i <= N; i += lowbit (i)) tr[i] += k; } int sum (int x) x++; int res = 0 ; for (int i = x; i; i -= lowbit (i)) res += tr[i]; return res; } void solve () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; s[i] = (s[i - 1 ] + a[i]) % m; } LL res = 0 ; for (int r = 1 ; r <= n; r++) res += 1ll * s[r] * r; for (int l = 1 ; l <= n; l++) res -= 1ll * s[l - 1 ] * (n - l + 1 ); LL cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cnt += (i - 1 - sum (s[i])); add (s[i], 1 ); } res += 1ll * m * cnt; cout << res << endl; } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }
F - Add One Edge 2 Problem:F - Add One Edge 2
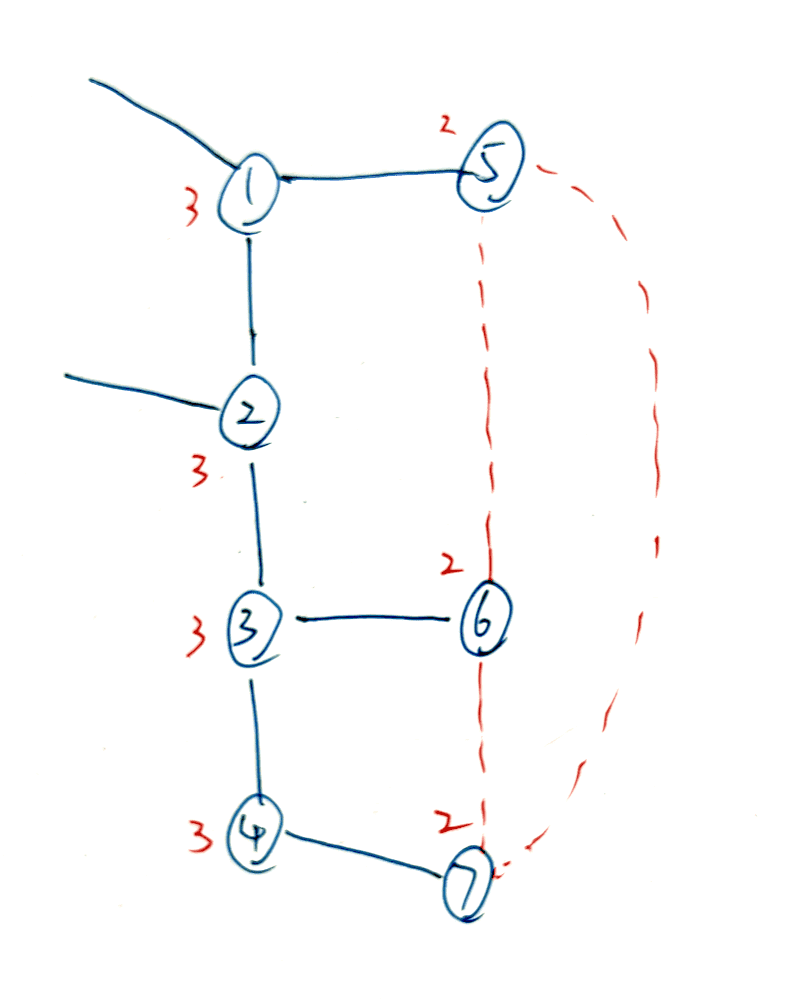
题目: 给定一个树,有 N 个节点,N-1 条边。
给树增加一条边,能把树变成恰好带一个环的图。
请问有多少个图满足条件:简单图,环上的所有顶点读数为 3。
约束条件:
思路: 这道题目结论比较暴力:
直接找度数为
由于是把所有的点都看过,所以极限状态下的时间复杂度为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 2e5 + 10 , M = 4e5 + 10 ;int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx; int n;int deg[N]; bool st[N]; int cnt; LL res; void add (int a, int b) e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++; } void dfs (int now, int fa = 0 ) if (deg[now] != 3 ) { cnt += (deg[now] == 2 ); return ; } st[now] = true ; for (int i = h[now]; i != -1 ; i = ne[i]) { int next = e[i]; if (next == fa) continue ; dfs (next, now); } } void solve () memset (h, -1 , sizeof h); cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i++) { int u, v; cin >> u >> v; add (u, v), add (v, u); deg[u]++, deg[v]++; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (deg[i] != 3 ) continue ; if (st[i]) continue ; cnt = 0 ; dfs (i); res += 1ll * cnt * (cnt - 1 ) / 2 ; } cout << res << endl; } int main () cin.tie (0 ); ios_base::sync_with_stdio (false ); solve (); return 0 ; }

![image-20241227153446971]()