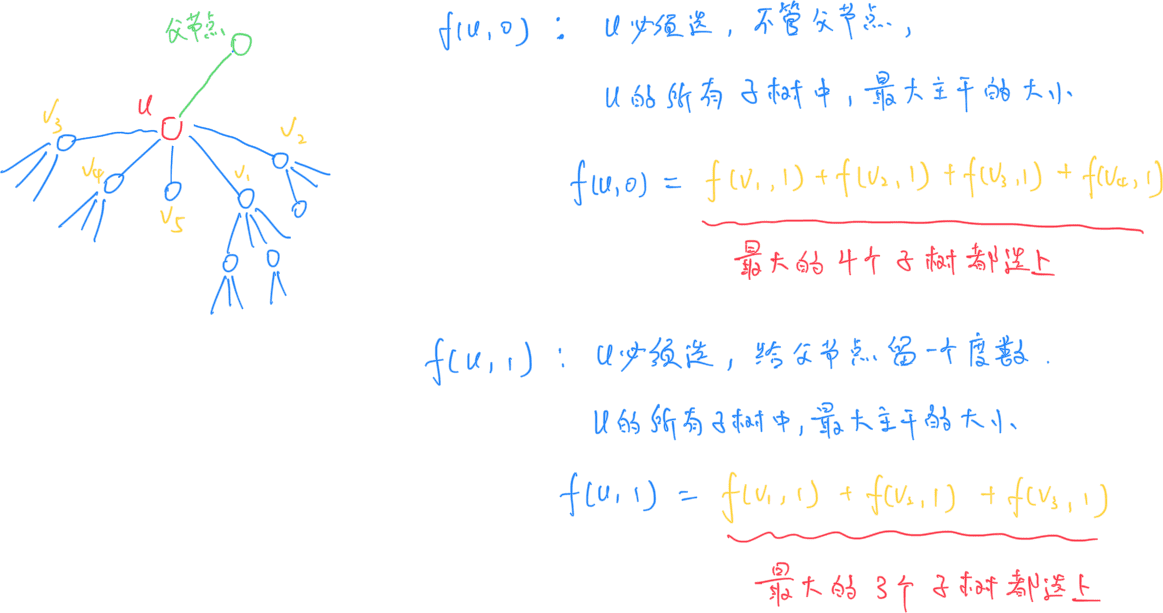本文是 AtCoder Beginner Conteset(ABC)394 的总结笔记。
A - 22222
Problem:A - 22222
模拟题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
string s;
int cnt;
void solve() {
cin >> s;
for (auto x : s)
if (x == '2')
cnt++;
cout << string(cnt, '2') << endl;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
return 0;
}
|
B - cat
Problem:B - cat
模拟题。
题目:
有 n 个字符串。把这些字符串按照长度,从小到大连接起来。
思路:
解法 1:
使用一个 PII 存储 {字符串长度,字符串编号},然后按照字符串长度升序排列,从前往后输出即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 55;
string s[N];
PII tmp[N];
int n;
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> s[i];
tmp[i] = {s[i].size(), i};
}
sort(tmp, tmp + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << s[tmp[i].second];
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
return 0;
}
|
解法 2:
自定义一个 cmp 算子。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 55;
int n;
string s[N];
bool cmp(string& a, string& b) {
return a.size() < b.size();
}
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> s[i];
sort(s, s + n, cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << s[i];
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
return 0;
}
|
C - Debug
Problem:C - Debug
双指针
题目:
字符串 S。把连续出现的 WA 替换为 AC,再输出。
约束条件:
S 长度最大
思路:
解法 1:从前往后
这道题实际上是找出连续出现的诸如 WWWWWA 串,改成 ACCCCC。
解法 2:从后往前
思路会更容易一些。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
string s;
void solve() {
cin >> s;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
int right = i;
if (s[i] == 'W') {
while (right + 1 < s.size() && s[right + 1] == 'W')
right++;
if (right + 1 < s.size() && s[right + 1] == 'A') {
string tmp = "A" + string(right + 1 - (i + 1) + 1, 'C');
s.replace(i, right + 1 - i + 1, tmp);
}
i = right;
}
}
cout << s << endl;
}
void solve2() {
cin >> s;
int n = s.size();
s = " " + s;
for (int i = n; i > 1; i--) {
if (s[i - 1] == 'W' && s[i] == 'A')
s[i - 1] = 'A', s[i] = 'C';
}
cout << s.substr(1) << endl;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve2();
return 0;
}
|
D - Colorful Bracket Sequence
Problem:D - Colorful Bracket Sequence
栈的使用
题目:
给定字符串 S,只包含 (, ), [, ], <, > 几种字符。
请问给定的括号之间是否能够闭合?
约束条件:
S 最长为
思路:
标准的栈的使用方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
stack<char> stk;
string s;
bool check(char x) {
if (x == ')' && stk.top() == '(')
return true;
else if (x == ']' && stk.top() == '[')
return true;
else if (x == '>' && stk.top() == '<')
return true;
else
return false;
}
void solve() {
cin >> s;
for (auto x : s) {
if (x == '(' || x == '[' || x == '<')
stk.push(x);
else {
if (stk.empty() || !check(x)) {
cout << "No" << endl;
return;
}
stk.pop();
}
}
cout << (stk.empty() ? "Yes" : "No") << endl;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
return 0;
}
|
E - Palindromic Shortest Path
Problem:E - Palindromic Shortest Path
BFS
题目:
给定 N 个节点的有向图。
使用邻接矩阵 C 来表示图。
- 如果为
-,表示节点 i 与节点 j 之间没有边 - 如果为小写字母,表示有一条节点
i 指向节点 j 的边,且边的代码为这个小写字母
对于每一个整数对,回答下面问题:
- 从 i 到 j,是否存在最短的回文串路径。如果存在,输出距离;如果不存在,输出
-1
约束条件:
思路:
这是一道思路有些抽象但是非常巧妙的 BFS题目。
如果我们希望 i -> j 之间能够连成回文串,那么一定会有下面条件成立:
i -> u(i 连向 u) 并且 v -> j(v 连向 j) 并且这两条边的字符相同u -> v (u 能够到达 v)并且本身就是回文串
所以我们实际上不断的向下迭代,最最基本的 u -> v 的元素,只可能是两种:
- u 与 v 相同,此时距离为 0
- u 与 v 连了一条边,此时距离为 1
![image-20250226013917672]()
使用 BFS 可以保证,第一次触达未接触的点时,他们的距离就是最短的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int INF = 1e9 + 10;
const int N = 110;
int n;
char s[N][N];
int res[N][N];
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> (s[i] + 1);
memset(res, 0x3f, sizeof res);
queue<PII> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
q.push({i, i});
res[i][i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (i == j || s[i][j] == '-')
continue;
q.push({i, j});
res[i][j] = 1;
}
while (q.size()) {
auto now = q.front();
q.pop();
int u = now.first, v = now.second;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (s[i][u] == '-' || s[v][j] == '-')
continue;
if (res[i][j] != 0x3f3f3f3f)
continue;
if (s[i][u] == s[v][j]) {
res[i][j] = res[u][v] + 2;
q.push({i, j});
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
cout << (res[i][j] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : res[i][j]) << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
return 0;
}
|
F - Alkane
Problem:F - Alkane
树形 DP + 贪心
题目:
当一个图满足下面条件时,定位为烷烃:
- 图是一棵无向树
- 每个顶点的度数为 1 或 4,且至少有一个顶点的度数是 4
有 N 个顶点的一棵无向树 T。判断 T 是否存在一个烷烃的子图。求该子图的最大顶点数。
约束条件:
思路:
问题拆分 1:
通过分析烷烃的结构,我们很容易发现下面的规律:
![image-20250226000349801]()
并且,哪怕结构形式变一下,也是相同的规律:
![image-20250226004932624]()
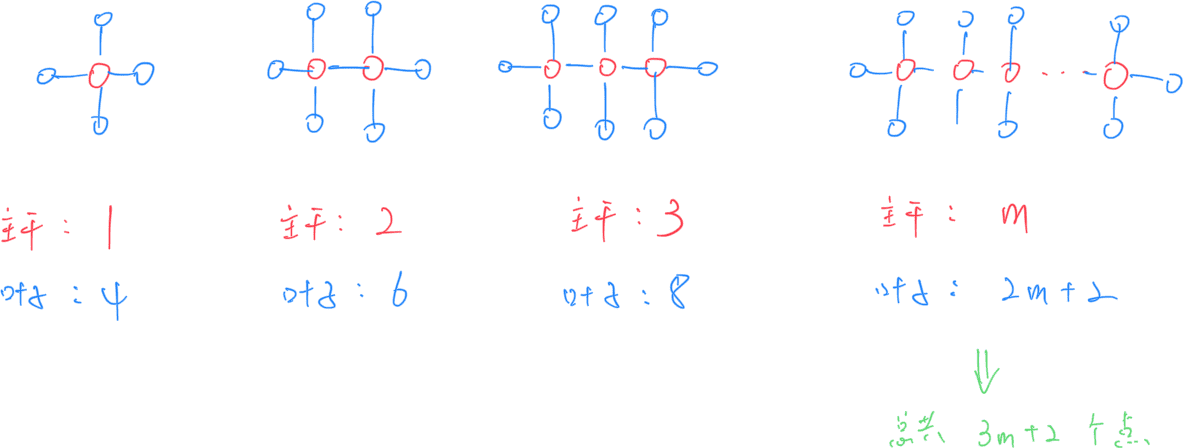
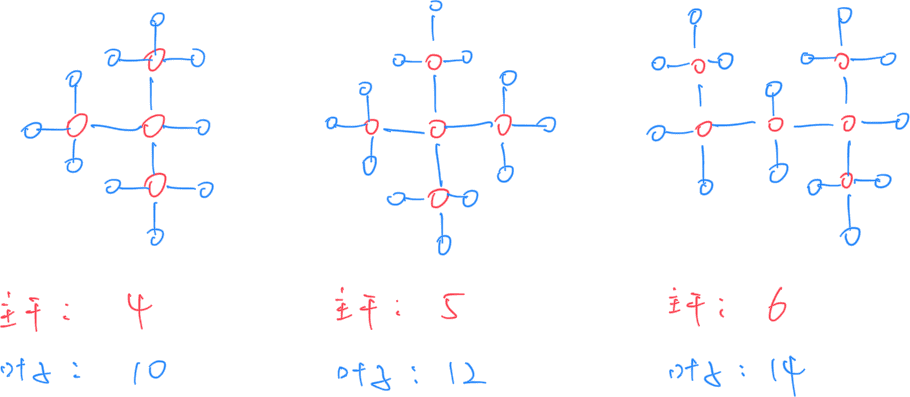
本题的问题可以转化为:原图中,能找到的度数等于 4 的点的最大连通块是多少。只要能找到这个最大的连通块(相当于知道了主干包含的点数 m),就可以计算出烷烃的最大顶点数为 3m+2
问题拆分 2:
那么这里有一个小问题。如果一个点的度数大于 4,这里我们肯定只会保留周围的 4 个节点,剩下的节点会被删掉。那么如何让保留下来的四个节点向外扩展的连通块最大呢?也就是说,如何找到最大主干的连通块呢?使用树形 DP。
![image-20250226011000176]()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n;
int u, v;
int d[N];
bool vis[N];
int f[N][2];
int res;
vector<int> g[N];
void dfs(int u) {
vis[u] = true;
vector<int> tmp;
for (int v : g[u])
if (d[v] >= 4 && !vis[v]) {
dfs(v);
tmp.push_back(f[v][1]);
}
sort(tmp.rbegin(), tmp.rend());
f[u][1] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < tmp.size() && i < 3; i++)
f[u][1] += tmp[i];
f[u][0] = f[u][1];
if (tmp.size() >= 4)
f[u][0] += tmp[3];
res = max(res, f[u][0]);
}
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
g[u].push_back(v), g[v].push_back(u);
d[u]++, d[v]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (d[i] >= 4 && !vis[i]) {
dfs(i);
}
}
if (res == 0)
cout << -1 << endl;
else
cout << res * 3 + 2 << endl;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
solve();
return 0;
}
|